BIOLOGY GRADE 12 - THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM - ETHIOPIA NEW CURRICULUM
Book Description
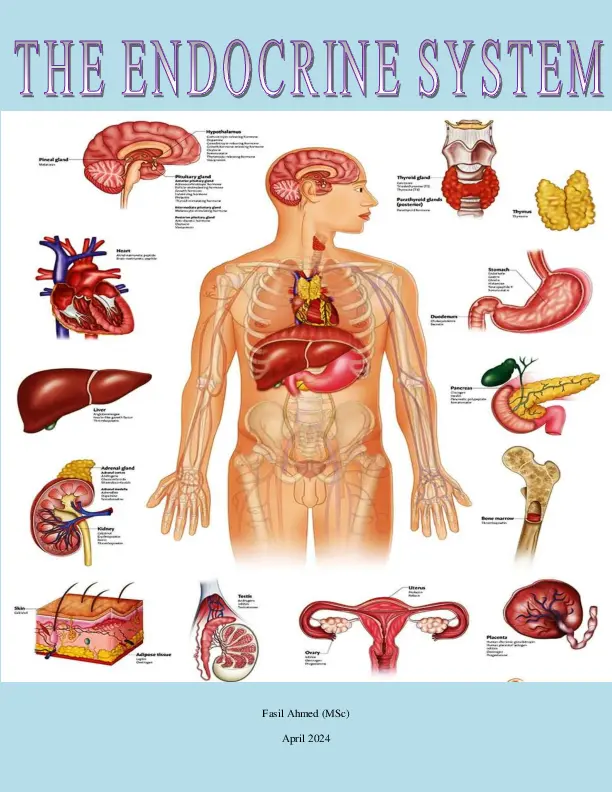
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Introduction The endocrine system is a network of glands and organs throughout the body that produce and release hormones.
The primary function of the endocrine system is to coordinate and regulate bodily processes such as metabolism, growth and development, reproduction, mood, and responses to stress.
The endocrine system is composed of glands and their chemical messengers called hormones.
Hormones Hormones are chemical messengers produced by glands and tissues in the body.
They are secreted into the bloodstream and travel to target cells or organs where they exert specific effects on physiological processes.
Hormones act as chemical messages, produced in one part of the body but having an effect somewhere entirely different.
Many processes in the body are coordinated by hormones.
Hormones play a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including metabolism, growth and development, reproduction, mood, and responses to stress.
Most hormones only affect certain tissues or organs (their target organ) and the hormone is picked up from the blood by receptors in the cell membranes.
Although hormones reach all parts of the body, only target cells with receptors respond.
They can have diverse effects depending on their type and target cells.
Some hormones stimulate certain activities, while others inhibit them.
Hormones work in concert with the nervous system to maintain homeostasis.
They can act rapidly but often slower and long lasting than the nervous system.
Hormonal signaling is essential for modulating long-term processes and maintaining overall bodily balance.
Examples of hormones include insulin, adrenaline, and estrogen and testosterone..
Courses
Education, BiologyReview Posted!
Add your details below to get email notifications when someone replies to your review.
Delete Comment?
This action cannot be undone. Are you sure?
Login
Still looking for something else?
Try this Advanced search Enhanced by Google
 Exotic Ai
Exotic Ai












Comment Section (0)
No reviews yet. Be the first!